A method in which the carrier gas is flown into the liquid tank and the vaporized precursor gas is transported to the chamber together with the carrier gas.
Bubbling method principle
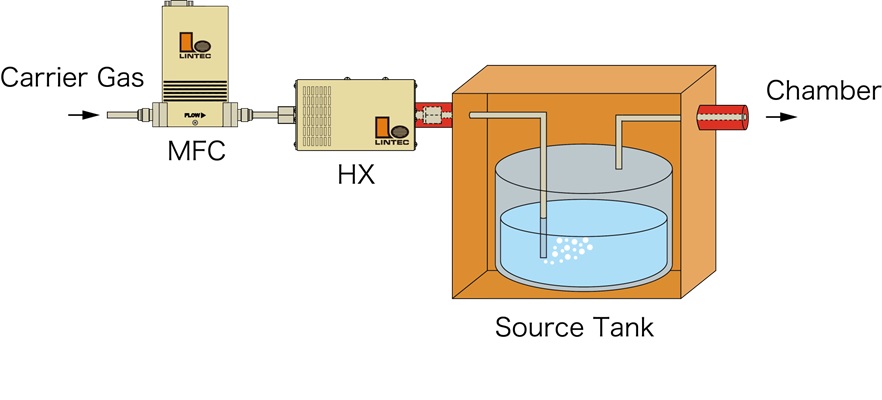
The concentration of liquefied gas is generally calculated as follows: vapor pressure (partial pressure) / tank pressure (total pressure) x 100 = liquefied gas concentration (%).
The flow rate of liquefied gas can be calculated as follows: liquefied gas concentration x carrier gas flow rate.
However, it is not easy to maintain a constant vapor pressure in a liquid tank where the carrier gas keeps flowing and the liquid temperature and surface area keep changing due to continuous vaporization.
Therefore, the direct vaporization method and the baking method were developed.
Features
- Can be used at low or atmospheric pressure
- Any liquid type can be used

