In the 1990s, when the semiconductor industry required a stable continuous vaporization supply system for TEOS, Lintec was the first in the world to develop a direct vaporization system using a vaporizer and liquid mass flow.
Basic Principles of Liquid Vaporization Technology
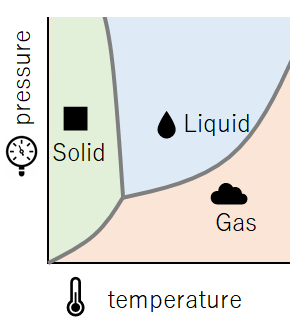
The three states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas, which change with temperature and pressure.
- Temperature approach:MFC baking method, non-carrier vaporizer
- Temperature and pressure approach:Direct vaporization method, bubbling method
- Pressure approach:Low differential pressure MFC (MC-3000S)
Vapor pressure and vapor concentration
The equation for gas concentration is as follows: “partial pressure ÷ total pressure × 100 = gas concentration (%)”.
The partial pressure of liquefied gas cannot exceed the vapor pressure curve.
Vapor pressure curve
The state of matter depends on temperature and pressure. When temperature is high, the force (vapor pressure) that causes a liquid to change to gas (vapor) increases, and when temperature is low, the vapor pressure decreases. The vapor pressure curve represents the maximum amount of vapor pressure at a given temperature.
Introduction of vaporization technology
Direct vaporization method
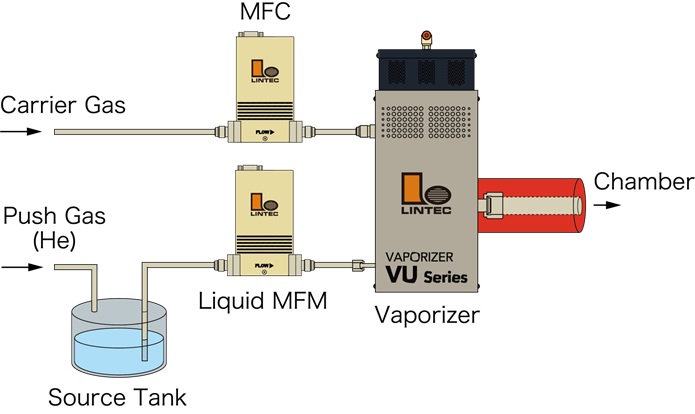
This method utilizes a mass flow meter to measure precursor flow rate and a vaporizer to control the flow rate and facilitate the vaporization process. It is widely used in CVD processes for many precursors, for example, TEOS.
Baking method
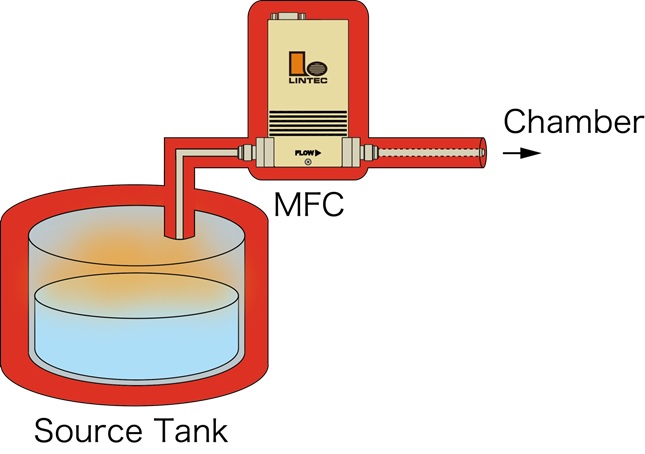
This method heats the liquid and controls the evaporated gas with a high-temperature gas mass flow controller. It is used in the manufacturing process of optical fiber etc.
Bubbling method
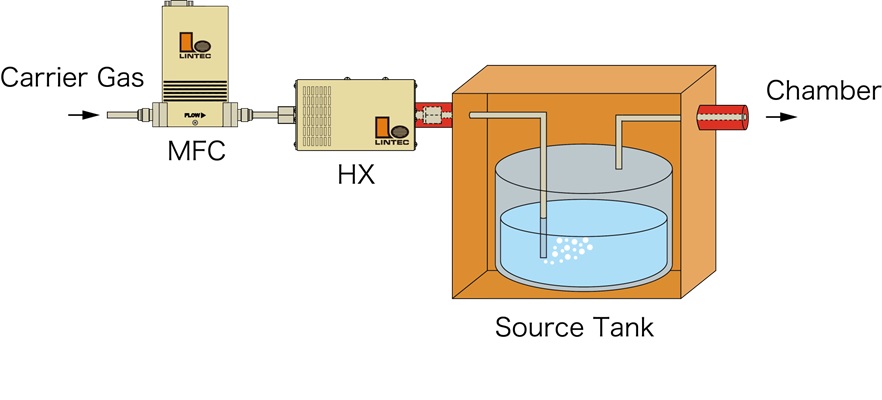
This method is conducted by integrating the vaporized gas into the carrier gas by passing the carrier gas through the liquid tank. Mainly used in MOCVD process.
Liquid Vaporized Feedstock Results
| Chemical Element | Abbreviation | Chemical Formula | CAS No. |
| Al | TMA | Al(CH3)3 | 75-24-1 |
| TEA | Al(C2H5)3 | 97-93-8 | |
| Al(MMP)3 | Al[CH3OCH2C(CH3)2O]3 | 478695-89-5 | |
| DMAH | H(CH3)2Al | 885-37-2 | |
| ASBO | Al[OCH(CH3)CH2CH3]3 | 2269-22-9 | |
| B | TEB | B(OC2H5)3 | 150-46-9 |
| TMB | B(OCH3)3 | 121-43-7 | |
| TMAB | B[N(CH3)2]3 | 4375-83-1 | |
| Ba | Ba(DPM)2 | Ba(C11H19O2)2 | 17594-47-7 |
| Bi | Bi(CH3)3 | 593-91-9 | |
| Ce | Ce(DPM)4 | Ce(C11H19O2)4 | 18960-54-8 |
| Cl | CCl4 | 56-23-5 | |
| C2H3Cl3 | 79-00-5 | ||
| C2Cl4 | 127-18-4 | ||
| Co | Co AMD | ||
| Cu | Cu(DPM)3 | Cu(C11H19O2)2 | 14040-05-2 |
| Cu(hfac)(TMVS) | C10H13CuF6O2 Si | 139566-53-3 | |
| Cu(EDMDD)2 | Cu[(CH3)3CC(O)CHC(O)CH(C2H5)C4H9] | ||
| Ga | TEG | (C2H5)3Ga | 1115-99-7 |
| TMG | (CH3)3Ga | 1445-79-0 | |
| Ge | Ge(OC2H5)4 | 14165-55-0 | |
| C4H12GeO4 | 992-91-6 | ||
| Hf | TDMAH | Hf[N(CH3)2]4 | 19782-68-4 |
| TEMAH | Hf[N(C2H5)CH3]4 | 352535-01-4 | |
| TDEAH | Hf[N(C2H5)2]4 | 19824-55-6 | |
| HTB | Hf(OtC4H9)4 | 2172-02-3 | |
| I | IF5 | 7783-66-6 | |
| In | In(acac)3 | In(C5H7O2)3 | 14405-45-9 |
| TMI | (CH3)3In | 3385-78-2 | |
| TEI | In(C2H5)3 | 923-34-2 | |
| La | La(TMOD)3 | ||
| Nb | PEN | Nb(OCH2CH3)5 | 3236-82-6 |
| Ni | Ni AMD | ||
| P | TMOP | PO(OCH3)3 | 512-56-1 |
| TEPO | PO(OC2H5)3 | 78-40-0 | |
| TMP | P(CH3O)3 | 121-45-9 | |
| Pb | Pb(DPM)2 | Pb(C11H19O2)2 | 21319-43-7 |
| Pb(thd)2 | |||
| Pb(TMOD)2 | |||
| Pr | Pr(EtCp)3 | Pr(C5H4C2H5)3 | 108-88-3 |
| Pr(DPM)3 | Pr(C11H19O2)3 | 15492-48-5 | |
| Pt | C9H16Pt | 94442-22-5 | |
| Ru | Ru(EtCp)2 | Ru(C2H5C5H4)2 | 32992-96-4 |
| DER | Ru(C7H9)(C7H11) | 501652-75-1 | |
| Si | TEOS | Si(OC2H5)4 | 78-10-4 |
| SiCl4 | 10026-04-7 | ||
| TCS | SiHCl3 | 10025-78-2 | |
| TMOS | Si(OCH3)4 | 681-84-5 | |
| HMDS | C6H19NSi2 | 999-97-3 | |
| HMDSO | C6H18OSi2 | 107-46-0 | |
| BTBAS | [(CH3)3CNH]2SiH2 | 186598-40-3 | |
| DIBDMS | C10H24O2Si | 17980-32-4 | |
| TMS | Si(CH3)4 | 75-76-3 | |
| DEMS | C5H14O2Si | 2031-62-1 | |
| C3H10Si | 993-07-7 | ||
| CH3Cl3Si | 75-79-6 | ||
| OMCTS、D4 | C8H24O4Si4 | 556-67-2 | |
| TMCTS | C4H16O4Si4 | 2370-88-9 | |
| TDMAS | SiH[N(CH3)2]3 | 15112-89-7 | |
| TMDS | C4H15NSi2 | 15933-59-2 | |
| C3H10O3Si | 2487-90-3 | ||
| [(CH2=CH)(CH3)SiO]4 | 2554-06-5 | ||
| VMDS | C5H12O2Si | 16753-62-1 | |
| DMDES | (CH3)2Si(OC2H5)2 | 78-62-6 | |
| DMPS | C8H12Si | 766-77-8 | |
| (CH3)Si(OCH3)3 | 1185-55-3 | ||
| C13H13F17O3Si | 83048-65-1 | ||
| C14H32O3Si | 2943-75-1 | ||
| Sn | SnCl4 | 7646-78-8 | |
| [CH3(CH2)3]4Sn | 1461-25-2 | ||
| Sn(C9H16O2)2 | 22673-19-4 | ||
| Sr | Sr(DPM)2 | Sr(C10H10F7O2)2 | 36885-30-0 |
| 280572-89-6 | |||
| Ta | PET | Ta(OC2H5)5 | 6074-84-6 |
| TBTEMT | Ta(NtC4H9)[N(C2H5)CH3]3 | 511292-99-2 | |
| TBTDET | T-BuN=Ta(NEt2)3 | 169896-41-7 | |
| Taimata | Ta[NC(CH3)2C2H5][N(CH3)2]3 | 440081-38-9 | |
| PDMAT | C10H30N5Ta | ||
| Ti | TiCl4 | 7550-45-0 | |
| TTIP | Ti(i-OC3H7)4 | 546-68-9 | |
| TDEAT | Ti[N(C2H5)2]4 | 4419-47-0 | |
| TEMAT | Ti[N(CH3)C2H5]4 | 308103-54-0 | |
| TDMAT | Ti[N(CH3)2]4 | 3275-24-9 | |
| Ti(iPrO)2(DPM)2 | Ti(C11H19O2)2(O-i-C3H7)2 | 144665-26-9 | |
| Ti(MMP)4 | |||
| V | VCl4 | 7632-51-1 | |
| V(NEtMe)4 | |||
| Y | Y(DPM)3 | Y(C11H19O2)3 | 15632-39-0 |
| Zn | DEZ | (C2H5)2Zn | 557-20-0 |
| Zn(OD)2 | [CH3COCHCO(CH2)3CH3]2Zn | ||
| Zr | TEMAZ | Zr[N(CH3)CH2CH3]4 | 175923-04-3 |
| TDEAZ | Zr[N(C2H5)2]4 | 13801-49-5 | |
| Zr(t-Obu)4 | Zr[OC(CH3)]4 | 2081-12-1 | |
| (C5H5)Zr[N(CH3)2]3 | 33271-88-4 | ||
| Zr(dmhd)4 | Zr(C18H30O4)2 | 69990-43-8 | |
| Zr(DPM)4 | Zr(C11H19O2)4 | 18865-74-2 | |
| Zr(TMOD)4 | |||
| Zr(MMP)4 |

